nenupy.io.tf_utils
Support to Time-Frequency data
|
Inverts the halves of each beamlet and reshape the array in 2D (time, frequency) or 4D (time, frequency, 2, 2) if this is an 'ejones' matrix. |
- class nenupy.io.tf_utils.ReducedSpectra(file_name)[source]
Bases:
object
- class nenupy.io.tf_utils.TFPipelineParameters(*parameters)[source]
Bases:
object
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.blocks_to_tf_data(data, n_block_times, n_channels)[source]
Inverts the halves of each beamlet and reshape the array in 2D (time, frequency) or 4D (time, frequency, 2, 2) if this is an ‘ejones’ matrix.
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.compute_spectra_frequencies(subband_start_hz, n_channels, frequency_step_hz)[source]
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.compute_spectra_time(block_start_time_unix, ntime_per_block, time_step_s)[source]
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.compute_stokes_parameters(data_array, stokes)[source]
data_array: >2 D, last 2 dimensions are ((XX, XY), (YX, YY))
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.correct_bandpass(data, n_channels)[source]
Correct the Polyphase-filter band-pass response at each sub-band.
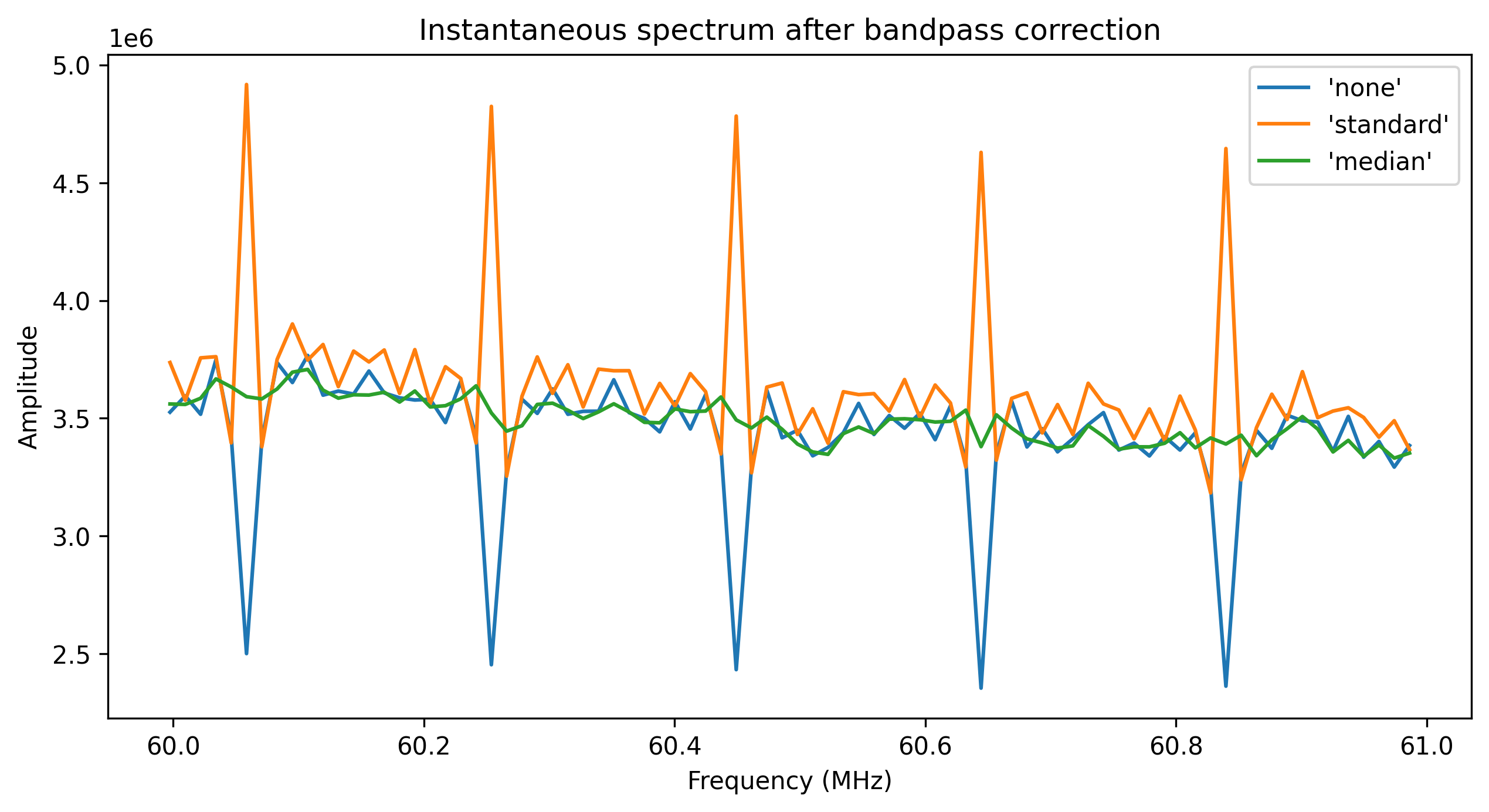
- Parameters:
data (np.ndarray) – _description_
n_channels (int) – _description_
- Raises:
ValueError – _description_
- Returns:
_description_
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.crop_subband_edges(data, n_channels, lower_edge_channels, higher_edge_channels)[source]
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.de_disperse_array(data, frequencies, time_step, dispersion_measure)[source]
De-disperse in time an array
datawhose first two dimensions are time and frequency respectively. The array must be regularly sampled in time. The de-dispersion is made relatively to the highest frequency. De-dedispersed array is filled withNaNin time-frequency places where the shifted values were.
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.plot_dynamic_spectrum(data, time, frequency, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs)[source]
_summary_
- Parameters:
data (np.ndarray) – _description_
time (Time) – _description_
frequency (u.Quantity) – _description_
fig (mpl.figure.Figure, optional) – _description_, by default None
ax (mpl.axes.Axes, optional) – _description_, by default None
- Returns:
_description_
- Return type:
Tuple[mpl.figure.Figure, mpl.axes.Axes]
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.remove_channels_per_subband(data, n_channels, channels_to_remove)[source]
Set channel indices of a time-frequency dataset to
NaNvalues. Thedataarray is first re-shaped as(n_times, n_subbands, n_channels, 2, 2)usingreshape_to_subbands().- Parameters:
- Raises:
TypeError – If
channels_to_removeis not of the correct type.IndexError – If any of the indices listed in
channels_to_removedoes not correspond to then_channelsargument.
- Returns:
Time-frequency correlations array, shaped as the original input, except that some channels are set to
NaN.- Return type:
- Example:
>>> from nenupy.io.tf_utils import remove_channels_per_subband >>> import numpy as np >>> >>> data = np.arange(2*4*2*2, dtype=float).reshape((2, 4, 2, 2)) >>> result = remove_channels_per_subband(data, 2, [0]) >>> result[:, :, 0, 0] array([[nan, 4., nan, 12.], [nan, 20., nan, 28.]])
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.reshape_to_subbands(data, n_channels)[source]
Reshape a time-frequency data array by the sub-band dimension. Given a
dataarray with one frequency axis of sizen_frequencies, this functions split this axis in two axes of sizen_subbandsandn_channels.- Parameters:
- Raises:
ValueError – _description_
- Returns:
_description_
- Return type:
-
- Example:
>>> from nenupy.io.tf_utils import reshape_to_subbands >>> import numpy as np >>> >>> data = np.arange(3*10).reshape((3, 10)) >>> result = reshape_to_subbands(data, 5) >>> result.shape (3, 2, 5)
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.sort_beam_edges(beam_array, n_channels)[source]
Find out where in the frequency axis a beam starts and end. This outputs a dictionnary such as: {
“<beam_index>”: (freq_axis_start_idx, freq_axis_end_idx,), …
}
- nenupy.io.tf_utils.spectra_data_to_matrix(fft0, fft1)[source]
fft0[…, :] = [XX, YY] = [XrXr+XiXi : YrYr+YiYi] = [ExEx*, EyEy*] fft1[…, :] = [Re(X*Y), Im(X*Y)] = [XrYr+XiYi : XrYi-XiYr] = [Re(ExEy*), Im(ExEy*)] Returns a (…, 2, 2) matrix (Dask)
ExEy* = (XrYr+XiYi) + i(XiYr - XrYi) EyEx* = (YrXr+YiXi) + i(YiXr - YrXi)